Have you ever felt that even a one‑second delay when opening an app is too slow? In 2026, that frustration is no longer just about processor speed, but about what experts call “cognitive latency.” Smartphones are evolving from reactive tools into anticipatory systems that prepare results before you even tap the screen.
With UFS 5.0 storage reaching up to 10.8GB/s, AI‑centric architectures in Android 16 and iOS 19, and predictive resource management powered by on‑device neural engines, mobile performance is being redefined at every layer. Hardware, operating systems, networks, and development frameworks are converging to eliminate not only physical delay, but perceived delay.
In this article, you will discover how next‑generation storage standards, proactive AI schedulers, WebTransport networking, and adaptive power management are working together to deliver near‑instant app launches. If you care about cutting‑edge gadgets and the future of mobile UX, this deep dive will show you why 2026 marks a true paradigm shift in mobile computing.
- From Reactive to Anticipatory: Why 2026 Redefines Mobile Performance
- UFS 5.0 and LPDDR6: Breaking the I/O Bottleneck with 10.8GB/s Storage
- Inline Hashing and Link Equalization: Security and Stability at Extreme Speeds
- Android 16’s AI Core: ART Optimization and Gemini-Powered Predictive Scheduling
- iOS 19 and Apple Intelligence: Liquid Glass Design Meets Proactive Memory Management
- Adaptive Resource Throttling (ART): Machine Learning for Real-Time Performance Control
- Cognitive Latency Reduction: Behavioral Biometrics and Invisible Authentication
- React Native’s New Architecture: Eliminating the Bridge for Faster Cold Starts
- Kotlin Multiplatform vs Native: What 2026 Benchmarks Reveal About Startup Speed
- Thermal Throttling, Compute Shaders, and the Physics of Sustained Performance
- Battery Health, Degradation Rates, and Their Hidden Impact on App Launch Speed
- 5G, WebTransport, and Edge Computing: Solving Network Latency at Scale
- Privacy, Transparency, and Trust in an AI-Driven Mobile Ecosystem
- 参考文献
From Reactive to Anticipatory: Why 2026 Redefines Mobile Performance
In 2026, mobile performance is no longer defined by how fast an app reacts after you tap it. It is defined by how rarely you need to wait at all. Smartphones have shifted from reactive tools to anticipatory systems that prepare outcomes before explicit input, fundamentally redefining what “fast” means.
According to JEDEC’s UFS 5.0 specification, sequential read speeds now reach up to 10.8GB/s, nearly doubling high-end UFS 4.0 implementations. Combined with LPDDR-class memory advancements, storage is no longer the primary bottleneck during cold starts. The constraint has moved from physical I/O to what experts call cognitive latency—the delay users perceive between intention and fulfillment.
2026 marks the year when perceived delay, not raw milliseconds, becomes the core performance metric.
| Era | Trigger Model | Primary Bottleneck | User Perception |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre‑2024 | User tap → System responds | Storage & CPU I/O | Visible loading screens |
| 2026 | System predicts → Prepares state | Cognitive latency | Instant contextual readiness |
Android 16 and iOS 19 embody this transformation. Both platforms integrate AI at the system core rather than as an application layer. Reports from WWDC and Google I/O 2025 highlight that predictive resource allocation now occurs before foreground execution. If a user routinely opens a transit app at 8:15 AM, the OS pre-warms its process, loads critical assets into memory, and stabilizes network connections in advance.
This anticipatory model is reinforced by communication advances. With mature 5G deployments reducing latency toward single-digit milliseconds and protocols such as WebTransport enabling out-of-order delivery, initial UI elements render even while secondary data streams continue in parallel. The experience feels instantaneous because the visible layer arrives first.
The breakthrough is architectural, not incremental. Adaptive Resource Throttling models dynamically allocate CPU, memory, and network budgets based on device state, battery temperature, and behavioral patterns. Instead of launching at full power every time, applications negotiate optimal readiness states that balance thermal stability and responsiveness.
Research into large-scale battery analytics, such as Geotab’s 22,700-vehicle study, shows how thermal conditions accelerate degradation. Mobile systems now incorporate similar intelligence, adjusting boost behavior during app initialization to avoid premature throttling. Performance is sustained not by brute force, but by predictive orchestration.
What truly distinguishes 2026 is that “launch time” is becoming invisible. Biometric context, behavioral cadence, and cached AI models complete authentication and personalization before the interface appears. By the time you see the screen, the system has already interpreted intent.
This shift from reaction to anticipation does more than accelerate apps. It transforms trust. When a device consistently aligns with user intention without friction, performance becomes a seamless extension of cognition itself.
UFS 5.0 and LPDDR6: Breaking the I/O Bottleneck with 10.8GB/s Storage
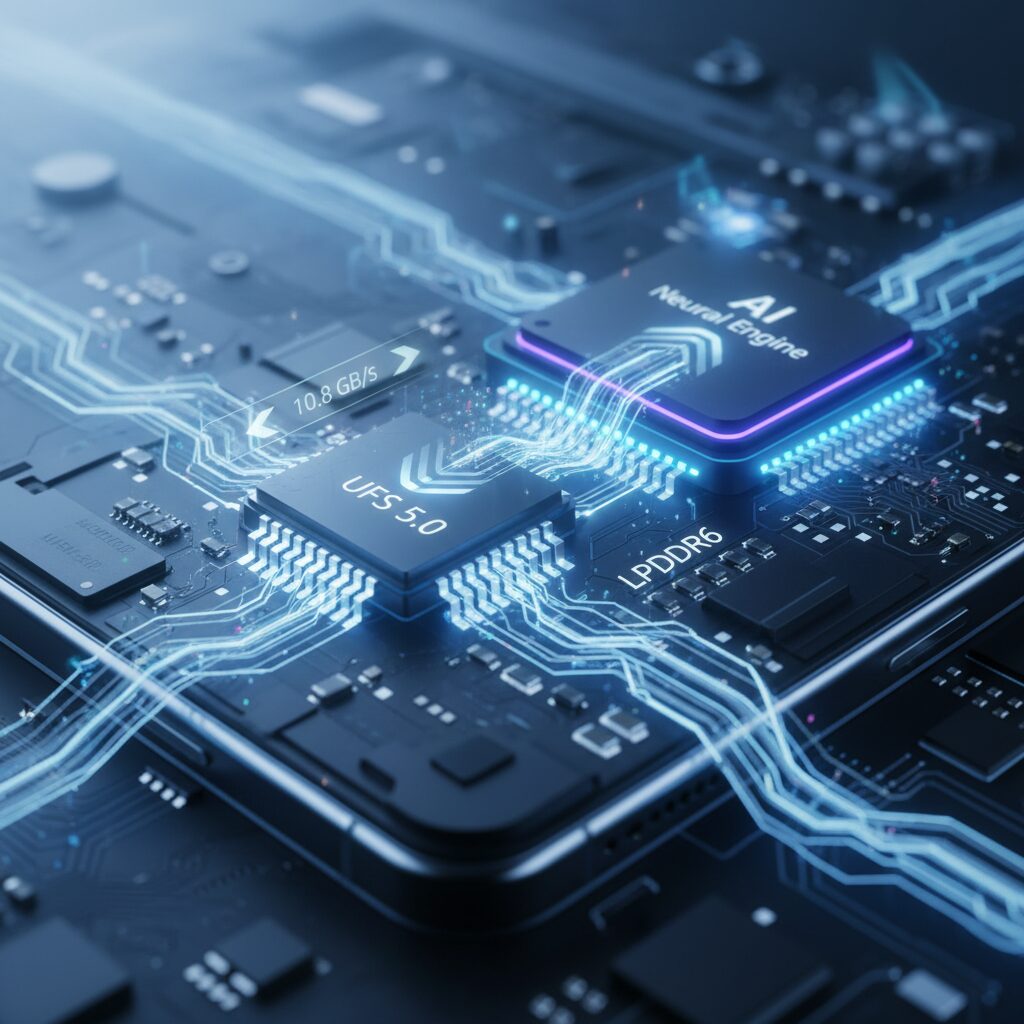
In 2026, the biggest invisible upgrade inside flagship smartphones is the leap to UFS 5.0 storage and LPDDR6 memory. As JEDEC defines in its latest specification, UFS 5.0 delivers up to 10.8GB/s of sequential read throughput, nearly doubling the upper range of UFS 4.0. This shift directly attacks the long-standing I/O bottleneck that limited how fast apps, AI models, and high-resolution assets could move between storage and memory.
The breakthrough is enabled by MIPI M-PHY v6.0 and the new High-Speed Gear 6 (HS-G6) mode. HS-G6 provides 46.6Gb/s per lane, and in a dual-lane configuration, it pushes mobile storage into performance territory once associated with PCIe 4.0 SSDs in PCs. According to coverage by PCMag and TechRadar, this level of bandwidth is not incremental evolution but a structural jump designed specifically for AI-centric workloads.
| Standard | Max Sequential Read | Physical Layer |
|---|---|---|
| UFS 4.0 | Up to 5.8GB/s | M-PHY v5.0 |
| UFS 5.0 | Up to 10.8GB/s | M-PHY v6.0 (HS-G6) |
For power users, this translates into dramatically faster cold starts. When an app needs to load hundreds of megabytes of pretrained AI weights into RAM, storage speed becomes the gating factor. With 10.8GB/s available, the time required to hydrate large language models or computational photography pipelines drops sharply, reducing the gap between tap and interaction.
UFS 5.0 also introduces inline hashing at the hardware level. This means data integrity checks occur during transfer rather than as a separate software step. The result is not only higher security but also lower overhead during massive file reads. Integrated link equalization further stabilizes high-speed signaling between SoC and storage, ensuring sustained throughput under heavy workloads.
However, storage alone cannot eliminate the I/O bottleneck. LPDDR6 plays a parallel role by increasing memory bandwidth and improving energy efficiency. As on-device AI inference becomes persistent rather than occasional, the speed at which data moves from UFS into RAM—and then across the memory bus to CPU, GPU, or NPU—determines whether performance feels instantaneous or constrained.
UFS 5.0 at 10.8GB/s combined with LPDDR6 bandwidth effectively turns storage from a bottleneck into an extension of high-speed working memory.
This architectural shift changes OS-level memory strategy. Instead of aggressively keeping all assets resident in RAM, systems can rely on ultra-fast demand paging. When storage latency approaches SSD-class performance, pulling data just-in-time becomes viable without perceptible delay. For AI-heavy applications, this means larger models can be staged dynamically rather than permanently occupying memory.
For gadget enthusiasts tracking raw specs, 10.8GB/s may look like just another number. In practice, it marks the moment mobile I/O throughput catches up with the computational ambitions of 2026 devices. As industry analysts note, modern smartphones are no longer limited by compute alone but by how quickly data can feed that compute. UFS 5.0 and LPDDR6 together redefine that balance, unlocking sustained, AI-driven performance without the historical drag of storage latency.
Inline Hashing and Link Equalization: Security and Stability at Extreme Speeds
At 10.8GB/s, UFS 5.0 is not just about raw throughput. The real breakthrough lies in how it preserves data integrity and signal stability while operating at speeds previously associated with high-end PCIe 4.0 SSDs. According to JEDEC’s published specification and coverage by PCMag and TechRadar, the jump from UFS 4.0 to UFS 5.0 nearly doubles peak sequential read performance. Without new safeguards, however, such speed would magnify corruption risks and transmission errors.
Inline Hashing and Integrated Link Equalization are the twin technologies that make extreme mobile storage speeds both secure and sustainable. They operate below the application layer, invisible to users, yet directly responsible for maintaining the “cognitive latency zero” experience modern AI-driven systems promise.
Inline hashing introduces hardware-level data integrity verification directly within the storage pipeline. Instead of relying solely on higher-level software checks, the controller computes and verifies hash values as data is written and read. This means corruption is detected in real time, not after the fact.
For AI-centric smartphones in 2026, this matters enormously. Large language models and computational photography stacks routinely load hundreds of megabytes during cold start. If even a small fragment is corrupted, startup failures or silent errors can occur. By embedding hashing directly into the storage workflow, UFS 5.0 reduces this risk without imposing additional CPU overhead.
PCMag notes that inline hashing is specifically designed to strengthen protection during high-speed transfers, where traditional error-checking mechanisms can become bottlenecks. Because the verification occurs inline—within the data path itself—it does not meaningfully extend latency. In practice, this preserves both speed and trust.
| Feature | Primary Function | User-Level Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Inline Hashing | Real-time integrity verification during transfer | Prevents corrupted AI models and app crashes |
| Link Equalization | Signal stabilization across high-speed lanes | Maintains consistent performance under load |
While hashing protects the data itself, link equalization protects the pathway. UFS 5.0 leverages MIPI M-PHY v6.0 and High-Speed Gear 6 (HS-G6), delivering up to 46.6Gb/s per lane. At these frequencies, signal degradation becomes a serious engineering challenge. Even microscopic impedance mismatches or thermal fluctuations can introduce bit errors.
Integrated link equalization dynamically compensates for these distortions. It adjusts signal characteristics to maintain clarity across the physical channel between processor and storage. In simpler terms, it ensures that what is transmitted at one end is received accurately at the other—even when the system is under sustained AI workloads.
This stability is critical during multitasking scenarios. Imagine a device simultaneously running on-device generative AI, capturing high-resolution computational photos, and synchronizing encrypted data in the background. Without equalization, sustained bandwidth could degrade, triggering retransmissions and perceived slowdowns.
Equalization reduces retransmission cycles, which directly lowers effective latency. For users, this translates into apps that feel instantly responsive even when the storage subsystem is saturated.
Another overlooked advantage is energy efficiency. Error correction and retransmission consume power. By stabilizing the link at the hardware level, equalization reduces wasted cycles. In AI-heavy smartphones where thermal headroom is limited, even marginal efficiency gains can delay thermal throttling. This indirectly protects app launch performance during extended sessions.
Security is also enhanced in subtle ways. Inline hashing strengthens defense against data tampering within the storage layer. While it is not a replacement for encryption, it ensures that stored AI weights, authentication caches, and system libraries remain unaltered during high-speed operations. For devices that rely on behavioral biometrics and predictive preloading, integrity verification becomes foundational.
Extremetech highlights that UFS 5.0 was designed explicitly to support next-generation AI workloads. Those workloads depend not only on bandwidth but on deterministic reliability. A predictive OS that preloads an app before you tap it cannot afford silent integrity faults. Inline hashing guarantees that what is preloaded is exactly what was intended.
From a systems architecture perspective, the combination of hashing and equalization enables more aggressive demand paging strategies. Because storage reads are both fast and trustworthy, operating systems can offload more data from RAM without sacrificing reliability. This reshapes memory management policies in Android 16 and iOS 19 environments, even though users never see the mechanism.
For developers and hardware enthusiasts, the takeaway is clear. Extreme speed alone does not define next-generation performance. Security and signal stability are prerequisites for sustained, real-world throughput. Without them, benchmark numbers would collapse under practical workloads.
Inline hashing ensures that every byte delivered at 10.8GB/s remains authentic and intact. Integrated link equalization ensures that the highway carrying those bytes stays stable under thermal and electrical stress. Together, they form the invisible infrastructure that allows AI-powered smartphones in 2026 to operate at SSD-class speeds without sacrificing reliability.
In the era of anticipatory computing, where systems act before users consciously command them, trust in the storage layer becomes non-negotiable. These technologies quietly guarantee that the speed you experience is not only fast—but fundamentally secure and stable.
Android 16’s AI Core: ART Optimization and Gemini-Powered Predictive Scheduling

Android 16 marks a structural shift in how performance is defined. Instead of merely accelerating app execution after a tap, the system reduces what researchers call cognitive latency—the gap between user intention and visible response. At the center of this shift is a deeply optimized Android Runtime (ART) working in tandem with system-level Gemini AI.
According to analyses published around Google I/O 2025 and subsequent platform reviews, the updated ART in Android 16 refines how bytecode is compiled, cached, and prioritized at runtime. Background tasks are no longer treated as static workloads. They are dynamically evaluated so that foreground applications receive preferential CPU cycles and memory allocation exactly when needed.
Android 16 does not simply run apps faster; it predicts which apps deserve to run first.
This intelligence is amplified by Gemini’s system integration. Unlike earlier assistant layers confined to messaging or search, Gemini now participates in scheduling decisions. If usage patterns show that a user opens a specific news or transit app every weekday morning, the system pre-warms that process before the screen is even unlocked. Required assets are fetched into cache, reducing perceived launch time to near zero.
The architectural interaction can be understood across three layers:
| Layer | Function | User Impact |
|---|---|---|
| ART Optimization | Dynamic compilation and memory prioritization | Smoother animations and reduced cold starts |
| Gemini Predictive Engine | Context-aware usage forecasting | Apps feel instantly available |
| Resource Scheduler | Foreground-first CPU and RAM allocation | Stable performance under load |
One visible extension of this philosophy is Live Updates, introduced in Android 16. Instead of forcing users to fully launch ride-hailing or delivery apps to check status, frequently refreshed information is surfaced directly on the lock screen and status bar. By minimizing unnecessary process activation, the system lowers total device load while improving responsiveness where it matters.
Industry commentary comparing Android 16 and iOS 19 highlights that Android’s strength lies in flexible task management and contextual AI integration. In practical terms, this means CPU bursts are aligned with predicted user intent rather than raw process priority alone. When memory pressure rises, ART reallocates resources without disrupting the active experience.
From a developer’s perspective, this changes optimization strategy. Instead of focusing solely on reducing binary size or initial load time, engineers must design apps that cooperate with predictive scheduling. Clean lifecycle management and efficient background behavior directly influence how often Gemini selects an app for proactive warming.
The result is a phone that appears to anticipate behavior rather than react to it. Android 16’s AI Core demonstrates that performance leadership in 2026 is defined less by clock speed and more by orchestration—where ART and Gemini collaborate to eliminate the sensation of waiting altogether.
iOS 19 and Apple Intelligence: Liquid Glass Design Meets Proactive Memory Management
iOS 19 marks a structural shift from reactive UI rendering to anticipatory system orchestration. With the introduction of the Liquid Glass design language, Apple does not merely refresh visuals; it re-architects how interface layers are composited and cached in memory.
Liquid Glass is tightly coupled with Apple Intelligence, enabling the system to predict which UI elements and app states should remain warm in memory based on context signals such as calendar events, location, and recent interactions.
This approach directly targets what researchers now describe as “cognitive latency” — the delay users perceive between intention and result.
| Component | Role in iOS 19 | Impact on Perceived Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Glass UI | Optimized compositing and fluid transitions | Smoother visual continuity during app switches |
| Apple Intelligence | On-device context prediction via NPU | Preloaded app states before user action |
| Adaptive Power Mode | AI-based thermal and battery balancing | Stable launch performance under load |
According to industry analyses comparing Android 16 and iOS 19, Apple’s emphasis lies in tightly integrated on-device AI execution rather than broad customization. The Neural Processing Unit continuously evaluates behavioral patterns without offloading sensitive data to external servers, reinforcing both responsiveness and privacy.
For example, if a user routinely opens a ride-hailing app after a specific meeting ends, iOS 19 can preload critical assets and authentication states moments before the meeting concludes. When the icon is tapped, the interface appears instantly because the memory allocation and data hydration have already occurred.
This is proactive memory management in practice. Instead of holding every app persistently in RAM, the system dynamically reallocates memory based on probabilistic intent modeling.
Such orchestration is made viable by modern storage speeds like UFS 5.0 reaching 10.8GB/s, as reported by JEDEC coverage in outlets such as PCMag and TechRadar. With near-SSD-class throughput, iOS 19 can aggressively purge inactive resources and reload them with negligible delay, balancing efficiency and readiness.
Adaptive Power Mode further refines this loop. When thermal pressure rises or battery health declines, AI determines whether to momentarily boost launch performance or execute a reduced-power initialization path. This prevents sudden throttling that would otherwise disrupt the illusion of fluidity.
The result is not simply faster app launches but a transformation of the interaction model itself. The system prepares before the tap happens. Liquid Glass provides the visual continuity, while Apple Intelligence ensures that memory, compute, and energy are aligned with predicted intent.
In iOS 19, speed is no longer measured only in milliseconds. It is measured in how invisible the waiting becomes.
Adaptive Resource Throttling (ART): Machine Learning for Real-Time Performance Control
Adaptive Resource Throttling (ART) represents a decisive shift from static performance tuning to real-time, machine learning–driven control. Instead of assigning a fixed memory or CPU budget at install time, ART continuously evaluates device conditions and dynamically reallocates resources to protect responsiveness at the exact moment users need it.
In 2026, this approach has become standard in performance-critical apps, particularly those loading large on-device AI models at launch. As noted in developer analyses on DEV Community, cross-device optimization now depends less on raw hardware power and more on contextual awareness across thermal, memory, and network layers.
At its core, ART processes multiple real-time signals before and during app launch. These inputs allow the system to decide whether to boost, maintain, or throttle workloads in order to minimize perceived delay without triggering instability.
| Signal | Why It Matters | Real-Time Action |
|---|---|---|
| Available Memory | Prevents foreground eviction or crashes | Reduce preloaded assets |
| Battery Temperature | Avoids thermal throttling | Lower rendering complexity |
| User Activity State | Foreground vs background priority | Reallocate CPU weight |
| Network Quality | Controls fetch latency | Adjust payload size |
Consider a device with low remaining battery and elevated thermal levels. Instead of launching at full graphical fidelity, an ART-enabled app may disable auto-playing media, defer nonessential API calls, or reduce shader intensity by up to 40 percent. This prevents startup hangs while preserving core functionality.
Machine learning models embedded in ART learn from behavioral patterns as well. If a user repeatedly opens a fintech app briefly to check balances, the system prioritizes lightweight UI rendering and cached summaries rather than loading full analytics dashboards. This reduces cold-start pressure on both memory and storage subsystems.
The impact is measurable in stability metrics. Developers report fewer out-of-memory terminations and reduced frame drops during launch on mid-tier 4GB RAM devices when ART logic is enabled. This is particularly important as hardware variance widens between entry models and 16GB flagship devices.
ART also interacts intelligently with modern storage speeds such as UFS 5.0. While 10.8GB/s sequential read capability dramatically reduces asset loading time, uncontrolled parallel reads can spike heat and power draw. ART moderates concurrency to maintain sustained performance rather than short-lived bursts.
Ultimately, Adaptive Resource Throttling is not about slowing applications down. It is about delivering the fastest experience that the device can sustain at that exact moment. By aligning computational intensity with real-world constraints, ART ensures that performance feels instant without sacrificing stability, battery health, or thermal safety.
For developers targeting 2026-era mobile platforms, integrating ART principles is no longer optional. It is the foundation for achieving near-zero cognitive latency in environments where user expectations tolerate no delay.
Cognitive Latency Reduction: Behavioral Biometrics and Invisible Authentication
In 2026, performance is no longer measured solely by milliseconds. The true benchmark is cognitive latency—the gap between a user’s intention and the system’s readiness to respond. As operating systems evolve into anticipatory platforms, authentication itself is becoming invisible, dissolving into the background before the user even realizes it was required.
Traditional login flows—password entry, fingerprint scan, facial recognition—introduced micro-frictions after an app launch. Even when technically fast, they imposed mental context switching. According to industry analyses highlighted in mobile AI development reports, reducing these interruptions significantly improves perceived speed and task completion rates, particularly in finance and healthcare applications where frequent authentication was once unavoidable.
Behavioral biometrics now address this challenge by authenticating users continuously and passively. Instead of asking, “Who are you?” the system evaluates, “Does this interaction pattern match you?” This shift enables authentication to complete before the user reaches a sensitive function.
| Signal Type | Collected Via | Authentication Role |
|---|---|---|
| Touch pressure & area | Capacitive display sensors | Distinguishes grip and finger geometry |
| Typing cadence | Keyboard input timing | Identifies rhythm and hesitation patterns |
| Device movement angle | Gyroscope & accelerometer | Recognizes habitual pickup motion |
These signals are processed locally through on-device machine learning models integrated into Android 16 and iOS 19 architectures. Because inference occurs on the NPU rather than the cloud, authentication decisions are made in milliseconds without network dependency. This aligns with broader 2026 mobile design principles emphasizing privacy-preserving, edge-based computation.
The practical impact is profound. In fintech apps, behavioral models can pre-validate a user during device wake-up. By the time the dashboard renders, identity confidence scoring has already exceeded the security threshold. The login screen never appears. Healthcare applications apply similar logic, verifying clinician access patterns while loading patient records, eliminating redundant biometric prompts during urgent workflows.
Invisible authentication does not remove security; it redistributes it across time. Instead of a single checkpoint, verification becomes continuous. If behavioral deviation exceeds acceptable variance—such as abnormal typing speed or grip orientation—the system can dynamically request secondary verification. This adaptive escalation balances usability and protection.
Research and industry commentary referenced in AI-driven mobile architecture discussions emphasize that reducing post-launch friction increases perceived responsiveness more effectively than raw processor gains alone. Users interpret uninterrupted flow as speed. In this sense, cognitive latency reduction becomes a UX discipline rather than a hardware race.
Another emerging layer is predictive UI restructuring. E-commerce platforms increasingly adjust navigation hierarchies based on sentiment signals, browsing history, and time-of-day behavior before the user taps the icon. When combined with invisible authentication, the experience feels instantaneous: identity confirmed, interface personalized, action ready.
Privacy remains central. Both Android and iOS ecosystems in 2026 highlight transparency dashboards that show sensor access in real time. Behavioral biometric data is typically stored as encrypted mathematical representations rather than raw motion or typing logs. This design reduces the risk of reconstructing personal activity while preserving model accuracy.
From a systems perspective, cognitive latency reduction represents the convergence of three forces: high-speed storage enabling rapid model loading, AI schedulers predicting user intent, and behavioral analytics authenticating silently. The result is not merely faster apps, but applications that feel pre-aligned with human rhythm.
For gadget enthusiasts and power users, this shift signals a deeper transformation. Performance optimization is no longer about benchmark scores. It is about eliminating the psychological pause between thought and execution. When authentication disappears into behavior itself, the device stops asking for permission and starts demonstrating understanding.
React Native’s New Architecture: Eliminating the Bridge for Faster Cold Starts
For years, React Native’s biggest performance bottleneck was the so-called “Bridge” that mediated communication between JavaScript and native modules. Every call had to be serialized, queued, and passed asynchronously across that boundary. This design was flexible, but it introduced measurable startup overhead—especially during cold starts, when dozens of modules initialize at once.
In the New Architecture, that Bridge is effectively eliminated. Instead of routing everything through a serialized message queue, React Native now relies on JSI (JavaScript Interface), TurboModules, and Fabric. The result is a more direct, synchronous, and memory-efficient execution model that significantly reduces cold start latency.
What Changed Under the Hood
| Legacy Architecture | New Architecture | Cold Start Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Asynchronous Bridge | JSI direct calls | Removes serialization overhead |
| Eager module loading | TurboModules (lazy) | Lower initial memory load |
| Old UI Manager | Fabric renderer | Faster UI mounting |
JSI enables JavaScript code to call native functions directly, without passing through a batched JSON bridge. This synchronous access dramatically reduces the initialization gap between the JS runtime and native layers. According to industry benchmarks summarized by IteratorsHQ in 2025, migrating to the New Architecture improved startup time by roughly 900ms on lower-end devices such as Fire HD tablets.
That improvement is not incremental—it is experiential. In a mobile ecosystem increasingly defined by “cognitive latency,” shaving nearly a second from cold start directly affects perceived intelligence and responsiveness.
TurboModules and Memory Discipline
Another major shift is the introduction of TurboModules. Instead of loading every native module during app initialization, modules are now lazily instantiated only when required. Reports indicate this approach can reduce memory consumption at launch by 20–30%, which is particularly impactful on 4GB RAM devices still common in emerging markets.
Lower memory pressure during cold start means fewer garbage collection cycles and reduced risk of early frame drops. This is crucial when paired with modern storage standards like UFS 5.0, where data can be read at up to 10.8GB/s. Faster I/O is only beneficial if the framework can ingest and bind that data without architectural friction.
The New Architecture aligns React Native with high-bandwidth storage and AI-heavy workloads. Without the Bridge bottleneck, large configuration files, preloaded AI assets, or feature flags can be initialized with near-native efficiency.
Fabric and Deterministic UI Mounting
Fabric replaces the legacy UI Manager with a concurrent, more predictable rendering pipeline. Because layout calculation and mounting are more tightly integrated with the native layer, the first meaningful paint during cold start occurs sooner. This is particularly important for apps that rely on complex navigation stacks or animated splash transitions.
Meta’s internal benchmarks, referenced in 2025 performance analyses, emphasize that the combination of JSI, TurboModules, and Fabric narrows the performance gap between cross-platform and fully native implementations. In practical terms, the startup experience now depends more on app design decisions than on framework limitations.
For performance-focused teams in 2026, the implication is clear: React Native is no longer inherently constrained by cross-thread message passing during cold start. The elimination of the Bridge transforms React Native from a convenience layer into a near-native execution environment, making it viable even for applications where sub-second startup is a competitive differentiator.
Kotlin Multiplatform vs Native: What 2026 Benchmarks Reveal About Startup Speed
In 2026, startup speed is no longer judged in isolation from the underlying OS and hardware stack. When comparing Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) and fully native implementations, recent benchmarks reveal a far more nuanced picture than the traditional “native is always faster” narrative.
A performance analysis published via Diva Portal in 2026 shows that KMP can outperform native implementations on iOS in specific startup scenarios, while demonstrating measurable overhead on Android. These findings challenge long‑held assumptions in cross‑platform strategy.
| Metric | KMP vs Native (iOS) | KMP vs Native (Android) |
|---|---|---|
| App Startup Speed | ~57% faster | ~44% slower |
| CPU Performance | ~81% faster | ~26% slower |
| Image Rendering | 58–83% faster | 58–83% faster |
On iOS, KMP’s shared business logic integrates efficiently with Apple’s memory management and ahead‑of‑time compilation model. Because the UI layer remains native (SwiftUI or UIKit), the startup-critical rendering pipeline is not abstracted away. In cold start conditions—especially where AI models or data parsing are involved—KMP’s optimized shared core can reduce initialization overhead.
By contrast, on Android 16 devices, startup penalties appear more frequently. The additional abstraction layer between shared Kotlin code and Android’s runtime environment can introduce measurable latency during process initialization. When combined with Android’s increasingly AI-driven scheduling and background prewarming mechanisms, even small inefficiencies become amplified in benchmark results.
However, raw percentage differences do not tell the whole story. In 2026, startup speed is tightly coupled with predictive OS behavior. Android 16’s Gemini-powered preloading and iOS 19’s Apple Intelligence frequently warm up processes before user interaction. In such environments, the gap between KMP and native can shrink in real-world usage compared to laboratory cold starts.
The key insight is that startup performance now depends on where the critical path resides. If heavy logic execution occurs before the first frame is drawn, KMP’s shared optimization may offer advantages—particularly on iOS. If platform-specific lifecycle handling dominates early execution, native Android implementations retain an edge.
Another factor is binary size and memory footprint. Larger binaries can increase load time from storage, even with UFS 5.0 delivering up to 10.8GB/s sequential read speeds, as reported by JEDEC-related coverage in PCMag and TechRadar. While modern storage minimizes I/O bottlenecks, memory pressure and initialization sequencing still influence perceived launch speed.
For performance-critical applications—such as fintech apps performing behavioral biometric checks at launch—the hybrid-native approach is gaining traction. Developers keep shared domain logic in KMP but implement startup-sensitive flows natively. This selective optimization strategy reflects what elite mobile teams now prioritize: minimizing cognitive latency rather than chasing synthetic benchmark wins.
Ultimately, 2026 benchmarks reveal that KMP is no longer a compromise framework. It is a strategic tool whose startup performance profile varies by platform. Choosing between KMP and native is less about ideology and more about understanding the startup execution graph on each OS—and optimizing precisely where milliseconds still matter.
Thermal Throttling, Compute Shaders, and the Physics of Sustained Performance
Even with UFS 5.0 storage reaching up to 10.8GB/s and increasingly intelligent OS schedulers, sustained mobile performance is ultimately constrained by physics. Thermal throttling remains the invisible ceiling that separates short bursts of speed from real-world stability.
Modern mobile CPUs and NPUs are designed for aggressive boost behavior. They can spike to high clock frequencies when launching an app or executing an AI inference task, but as heat accumulates inside a tightly sealed chassis, the system must reduce frequency and voltage to prevent damage.
According to optimization guidelines discussed in recent 2026 developer performance briefings, prolonged high-load compute—such as on-device ML inference, real-time image filtering, or large data parsing—can trigger frequency scaling within minutes if heat dissipation is insufficient. This is not a software flaw; it is thermodynamics.
| Component | Strength | Thermal Behavior Under Sustained Load |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | High single-thread burst | Rapid heat buildup, early throttling |
| GPU | Massive parallelism | More heat-efficient per operation |
| NPU | AI-specific acceleration | Efficient but workload-dependent |
This is where compute shaders become strategically important. By leveraging GPU compute pipelines through Metal on iOS and Vulkan on Android, developers can offload non-graphical workloads—such as matrix transformations or signal filtering—to hardware optimized for parallel throughput.
GPUs often complete parallelizable workloads at lower thermal cost per unit of computation compared to CPUs running scalar-heavy loops. As a result, total system temperature rises more slowly, delaying or even avoiding throttling events.
Industry performance guidance published in 2026 emphasizes that distributing workloads across heterogeneous cores—rather than saturating the CPU—can maintain frame pacing and input responsiveness during extended sessions. This is particularly critical in AI-assisted apps where inference may run continuously in the background.
The physics behind this is straightforward. Heat generation scales with power consumption, and power increases roughly with the square of voltage. Sustained high clocks demand higher voltage, which accelerates thermal saturation. Once internal temperature thresholds are crossed, the OS enforces dynamic frequency scaling to stabilize the system.
By contrast, compute shaders operate on thousands of lightweight threads simultaneously, allowing each unit to run at lower frequency while maintaining aggregate throughput. This architectural efficiency translates directly into steadier surface temperatures and more predictable performance curves.
In practice, this means an app that intelligently routes heavy numerical preprocessing to the GPU may launch slightly slower in synthetic benchmarks but remain consistently responsive after ten minutes of continuous use. For real-world users, sustained smoothness matters more than peak milliseconds.
Thermal throttling is therefore not merely a hardware limitation; it is a design parameter. Developers who understand the thermodynamic envelope of mobile silicon—and who strategically employ compute shaders—can shape performance profiles that feel instant not just once, but continuously.
Battery Health, Degradation Rates, and Their Hidden Impact on App Launch Speed
Even in an era of UFS 5.0 storage and AI-driven preloading, battery health quietly shapes how fast your apps actually launch. The missing link is not raw performance, but power delivery stability. When a battery degrades, peak power output drops—and the OS compensates by throttling performance at the exact moment an app needs a burst of energy.
According to a large-scale analysis of 22,700 electric vehicle batteries published by Geotab, lithium-ion batteries degrade at an average rate of 2.3% per year, with heat and charging habits being major accelerators. While smartphones operate on a different scale, the chemistry is similar, and the degradation dynamics follow comparable patterns.
As internal resistance increases over time, voltage sag becomes more pronounced during high-load events such as cold app launches, AI model initialization, or GPU-accelerated rendering. Modern mobile operating systems detect this instability and proactively reduce CPU and GPU frequencies to prevent shutdowns.
| Degradation Factor | Impact on Battery Health | Effect on App Launch |
|---|---|---|
| High-temperature usage | +0.4% annual acceleration | Earlier thermal throttling |
| Frequent fast charging | +1.0% annual acceleration | Reduced peak power delivery |
| Deep discharge cycles | Faster capacity fade | Increased launch instability |
| Temperature management | Reduced to 1.4–1.5% | More consistent burst performance |
What makes this critical in 2026 is the nature of modern workloads. Launching an AI-enhanced app may involve loading hundreds of megabytes into RAM and activating on-device neural processing. That initial spike demands short, intense power delivery. A battery at 85% state of health may still last all day, but it may no longer sustain the same instantaneous wattage as when new.
Apple’s Adaptive Power strategies and similar Android battery intelligence systems respond dynamically. If the system detects degraded capacity or rising internal resistance, it may smooth out power draw during launch sequences. The user perceives this as a slightly longer animation or delayed interactivity rather than a crash.
In other words, battery degradation does not just shorten endurance—it reshapes the performance envelope of your device.
Heat compounds the issue. As documented in performance optimization guides such as Ultrabookreview’s thermal analysis research, sustained thermal stress increases throttling frequency. On smartphones, this means that a device with both aged battery chemistry and elevated temperature will hit performance ceilings faster during repetitive app switching.
The hidden cost appears in cumulative micro-delays. An extra 150–300 milliseconds added to cold starts may seem negligible, but in professional or high-frequency usage patterns, those delays accumulate into perceptible friction.
Forward-looking systems mitigate this through predictive charging limits, background thermal calibration, and AI-managed discharge curves. By learning user charging routines—such as pausing at 80% overnight and completing the charge just before wake-up—devices reduce long-term chemical stress while preserving burst capacity for demanding tasks.
For power users and developers alike, the takeaway is clear: battery health is now a performance variable, not merely a longevity metric. Monitoring state of health, managing heat exposure, and moderating aggressive fast-charging habits directly influence how instantly your apps respond—especially in an AI-first mobile ecosystem where launch speed depends on stable, high-intensity power delivery.
5G, WebTransport, and Edge Computing: Solving Network Latency at Scale
In 2026, network latency is no longer treated as a minor inconvenience but as a structural bottleneck that directly shapes user perception. According to industry analyses cited by TestMu AI and other mobile trend reports, more than 50% of what users perceive as “app slowness” is rooted in network wait time rather than device performance. This is precisely where 5G, WebTransport, and edge computing converge to redefine responsiveness at scale.
The shift is not just about faster bandwidth, but about collapsing distance, protocol overhead, and queuing delays simultaneously.
5G: From 50ms to Near-Real-Time
By 2026, global 5G subscriptions are projected to approach 5.9 billion, marking the transition from rollout to maturity. Latency that once hovered around 50ms in typical 4G environments can now approach 1ms under ideal 5G conditions. This reduction fundamentally changes application design assumptions.
For cloud-synced productivity apps, multiplayer gaming, or AI-assisted navigation, the difference between 50ms and 1ms determines whether interactions feel reactive or instantaneous. Developers can now offload heavier inference tasks to the cloud without degrading perceived fluidity, provided network quality remains stable.
| Network Generation | Typical Latency | User Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 4G LTE | ~50ms | Noticeable delay in real-time sync |
| 5G | ~1ms (ideal) | Near-instant feedback and streaming |
However, raw latency improvements alone do not eliminate blocking behavior at the protocol layer. That is where WebTransport plays a decisive role.
WebTransport: Eliminating Head-of-Line Blocking
WebTransport, built on QUIC, enables unidirectional streams and out-of-order delivery. Unlike traditional HTTP models, applications are no longer forced to wait for sequential packet completion before rendering critical UI components.
This means partial data can be processed immediately, dramatically improving perceived load speed even in unstable network conditions.
For example, during app startup, configuration files, UI assets, and personalization data can stream independently. If one packet is delayed, others continue flowing. The result is a UI that appears “ready” before all background resources have fully synchronized.
Edge Computing: Processing Closer to Intent
Edge computing completes the triangle by relocating compute resources geographically closer to users. Instead of routing every request to distant centralized data centers, latency-sensitive workloads are processed at regional or carrier-level edge nodes.
In smart home ecosystems—where more than 750 million devices are connected via platforms like Google Home—edge synchronization allows state data such as lock status or temperature readings to update continuously in the background. When users open the companion app, they interact with pre-synchronized data rather than triggering a fresh cloud fetch.
This architectural shift transforms network latency from a blocking event into a background process. The app feels instant not because data travels infinitely fast, but because it has already been prepared closer to the user.
At scale, the synergy of 5G’s ultra-low latency, WebTransport’s parallelized streaming, and edge computing’s proximity processing enables what can be described as “network transparency.” The network no longer announces itself through loading spinners or frozen states. Instead, it fades into the infrastructure layer—precisely where high-performance mobile systems in 2026 are designed to keep it.
Privacy, Transparency, and Trust in an AI-Driven Mobile Ecosystem
As mobile systems become anticipatory rather than reactive, privacy, transparency, and trust move from secondary considerations to core architectural requirements. When Android 16 and iOS 19 proactively warm up apps, preload AI models, and analyze behavioral signals, users inevitably ask a critical question: how much does my device know about me?
In an AI-driven ecosystem, performance gains are only sustainable if users trust the invisible processes running beneath the surface. This is especially true as on-device intelligence expands into scheduling, authentication, and contextual prediction.
Both major platforms have responded by embedding privacy controls directly into system-level design. Features such as Privacy Hubs and real-time sensor indicators visualize when microphones, cameras, or location data are accessed, transforming abstract data flows into observable events.
| Area | Android 16 | iOS 19 |
|---|---|---|
| AI Processing | Gemini integration with system-level controls | Apple Intelligence with on-device NPU focus |
| Sensor Transparency | Real-time access dashboard | Visual indicators and permission summaries |
| Power & Data Governance | Context-aware resource management | Adaptive Power Mode with usage insights |
Apple has consistently emphasized on-device processing to minimize external data transfer, and industry analyses of iOS 19 highlight how Apple Intelligence prioritizes local inference whenever possible. This architectural decision reduces reliance on cloud calls, lowering exposure risk while also cutting latency.
Google, meanwhile, integrates Gemini at the system layer but pairs it with granular permission management and contextual disclosures. According to comparative OS reviews in 2026, the visibility of background activity has become a competitive differentiator rather than a compliance checkbox.
Transparency is not only about dashboards. It is about explainability. When predictive engines preload a commuting app before the screen is unlocked, users should understand that this action is based on recurring time and location patterns, not invasive data harvesting.
Academic research in human-computer interaction has long shown that perceived control strongly correlates with technology adoption. In a proactive mobile environment, this principle becomes even more important because AI operates before explicit commands are given.
Japan’s 2026 market context underscores this dynamic. Industry commentary notes that as digital optimization accelerates, alignment with local expectations around privacy and operational clarity becomes decisive. For users managing work manuals or sensitive financial data on smartphones, even a one-second predictive advantage must not compromise data integrity.
Hardware innovations such as UFS 5.0 also intersect with trust. Inline hashing at the storage level enhances data integrity during high-speed transfers, ensuring that rapid AI model loading does not introduce corruption risks. When performance and security scale together, users do not have to choose between speed and safety.
Ultimately, an AI-driven mobile ecosystem succeeds not because it predicts flawlessly, but because it communicates honestly. Predictive scheduling, adaptive power control, and behavioral authentication can feel seamless only when users remain confident that their data is processed responsibly, visibly, and primarily on their own devices.
In 2026, trust itself becomes a performance metric. The faster systems anticipate our needs, the more essential it is that privacy safeguards are equally anticipatory, transparent, and user-centric.
参考文献
- ExtremeTech:New UFS 5.0 Boasts 10.8GB/s Max Speed for Next-Gen AI Phones
- PCMag:UFS 5.0 Storage Is Official, and It’s Almost Twice as Fast to Help Power AI
- TechRadar:Smartphone storage just hit warp speed as UFS 5.0 aims to crush PCIe 4.0 SSDs and supercharge AI performance
- Cashify Blog:Android 16 Vs iOS 19: The 2026 Winner Isn’t Who You Think
- Diva-Portal:Kotlin Multiplatform vs Native Development: A Performance Analysis for Android and iOS
- Geotab:EV Battery Health: Key Findings from 22,700 Vehicle Data Analysis
- Google Home Developers:Google I/O 2025
